In the exciting world of cryptocurrency, have you ever wondered, “What is a blockchain in crypto?” Well, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets behind this revolutionary technology!
Imagine a digital ledger that keeps track of all transactions in a decentralized and transparent manner. That’s precisely what a blockchain is! It’s like a secure and unchangeable record book that everyone in the crypto community can access.
But wait, there’s more! Blockchain is not just about money. It has the power to transform various industries like supply chain management, healthcare, and even voting systems. So buckle up, because we’re about to embark on a fascinating journey into the world of blockchain in crypto!
Wondering what blockchain is in the world of cryptocurrency? In simple terms, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures transparency, security, and immutability. When a transaction occurs, it is added to a block and connected to previous blocks, creating a chain of information. This technology powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, revolutionizing the way we conduct financial transactions. Embrace the power of blockchain in the crypto world!
Contents
- 1 What Is a Blockchain in Crypto?
- 2 The Fundamentals of Blockchain
- 3 Key Takeaways: What Is a Blockchain in Crypto?
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 1. How does a blockchain work in cryptocurrency?
- 4.2 2. What are the benefits of using blockchain in crypto?
- 4.3 3. Are all cryptocurrencies based on blockchain technology?
- 4.4 4. What is the role of miners in the blockchain?
- 4.5 5. Can blockchain be hacked?
- 4.6 Blockchain And Cryptocurrency Explained In 10 Minutes | Blockchain And Cryptocurrency | Simplilearn
- 5 Summary
What Is a Blockchain in Crypto?
Welcome to the world of cryptocurrencies! If you’re new to the game, you’ve probably come across the term “blockchain” more times than you can count. But what exactly is a blockchain in crypto, and why is it such a significant concept? In this article, we will dive into the depths of blockchain technology and explore how it revolutionizes the world of cryptocurrencies. So sit back, relax, and get ready to unravel the mysteries of the blockchain!
The Fundamentals of Blockchain
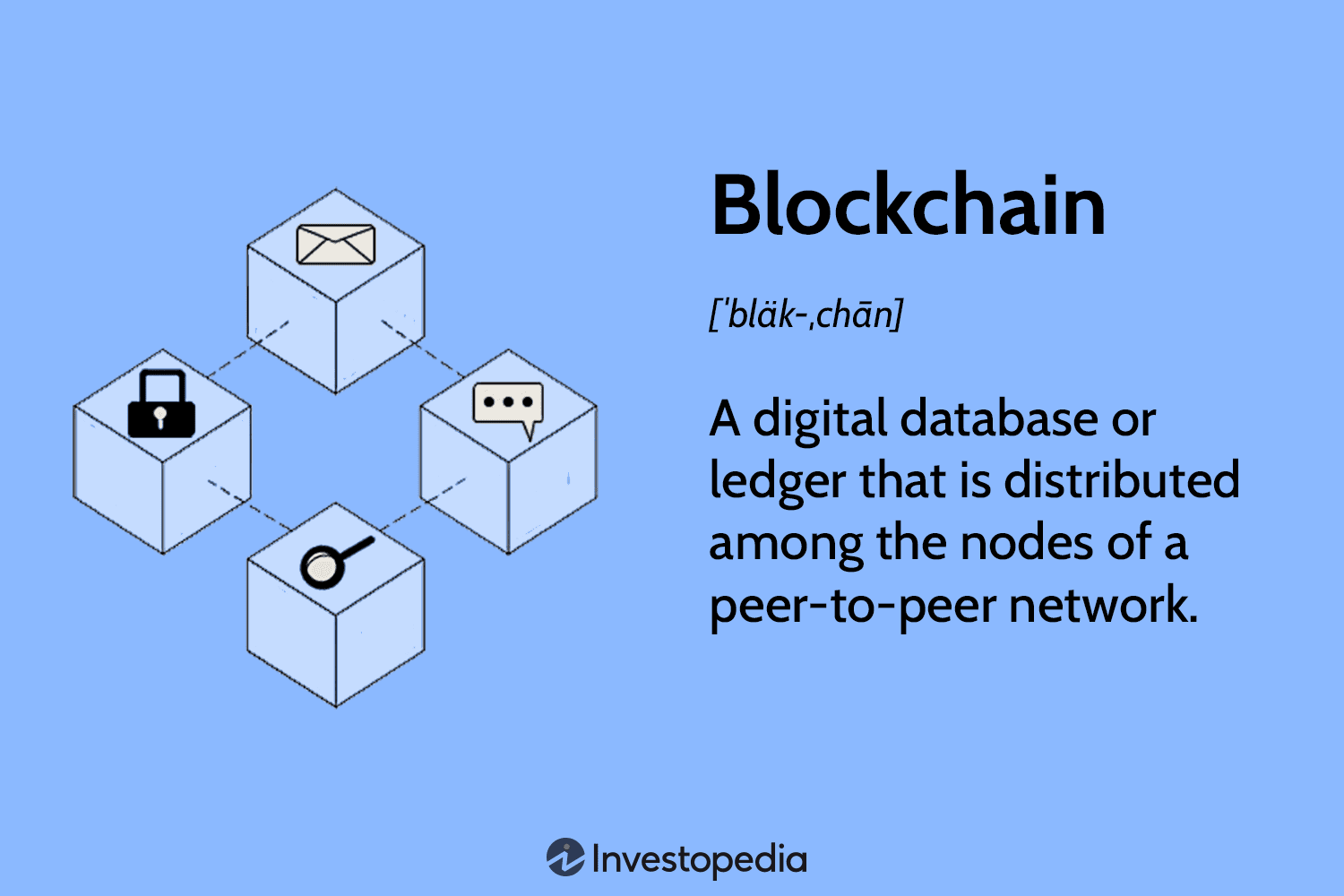
The blockchain is essentially a decentralized and transparent digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries such as banks or governments. At its core, the blockchain is a database composed of blocks that contain a list of transactions. Each block is connected to the previous block through a cryptographic hash, forming a chain of blocks – hence the name “blockchain.”
The blockchain has three essential characteristics that differentiate it from traditional databases. Firstly, it is decentralized, meaning no single entity has control over the entire network. Secondly, it is immutable, meaning that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with. Finally, it is transparent, as every transaction is visible to every participant on the network.
The blockchain revolutionizes the way transactions are conducted, eliminating the need for intermediaries and introducing a level of trust and transparency previously unseen in financial systems. Now that we have understood the fundamentals, let’s explore the different types of blockchains in the crypto world.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to anyone and are the most well-known type of blockchain. They allow anyone to join the network, participate in the consensus process, and validate transactions. Bitcoin, the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, is built on a public blockchain. These blockchains are highly decentralized, as they are maintained and run by a network of anonymous participants known as miners.
Achieving consensus on a public blockchain is done through a process called mining, which involves solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. The miners are rewarded with newly minted coins for their efforts. Examples of public blockchains include Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Litecoin.
Public blockchains offer several benefits, including security, transparency, and tamper-proof records. However, they often suffer from scalability issues due to the enormous computational power required for mining, resulting in slower transaction speeds.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are restricted to a specific group of participants who are granted access to the network. Unlike public blockchains, which are open to anyone, private blockchains are often used in enterprise settings. These blockchains are operated by a central authority or a consortium of trusted entities.
Private blockchains prioritize scalability, privacy, and efficiency over decentralization. They can process transactions faster since they are maintained by a limited number of participants. However, these blockchains sacrifice the transparency and openness of the public blockchain, as they require permission to join the network and participate in consensus.
Private blockchains are commonly utilized in industries such as banking, supply chain management, and healthcare, where privacy and control are paramount. Examples of private blockchains include Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum, and Corda.
Hybrid Blockchains
As the name suggests, hybrid blockchains combine the characteristics of both public and private blockchains. They aim to strike a balance between decentralization and scalability. In a hybrid blockchain, certain aspects are made public, such as transaction records, while other elements remain confidential.
Hybrid blockchains are often employed in scenarios where transparency and privacy coexist. They enable multiple organizations to interact and share data while maintaining privacy and confidentiality. One example of a hybrid blockchain is the Binance Chain, which combines both public and private elements to facilitate trading on the Binance platform.
Hybrid blockchains offer the advantages of both public and private blockchains, allowing for faster transaction speeds and permissioned access while still maintaining transparency and immutability.
The Future of Blockchain in Crypto
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the world of cryptocurrencies, but its potential reaches far beyond digital currencies. In recent years, blockchain has found applications in various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. The ability to create transparent, secure, and tamper-proof records opens up a world of possibilities for industries seeking improved efficiency and trust.
As blockchain continues to evolve, advancements in scalability and interoperability are being made to address the challenges faced by current blockchain networks. Additionally, governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to embrace blockchain technology, recognizing its immense potential in streamlining processes and combating fraud.
In conclusion, a blockchain in crypto is a decentralized, transparent, and immutable digital ledger that forms the backbone of cryptocurrencies. Whether it’s the public, private, or hybrid variety, the blockchain has transformed the way transactions are conducted and has the potential to disrupt various industries. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be exciting to witness the many innovative applications that blockchain brings to the table.
Key Takeaways: What Is a Blockchain in Crypto?
- A blockchain is a digital database that records and verifies transactions across multiple computers.
- Blockchains are designed to be secure, transparent, and decentralized.
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are built on blockchain technology.
- Blockchains use cryptographic algorithms to ensure the integrity of the data.
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries beyond cryptocurrencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Blockchain technology is a fundamental part of the cryptocurrency world. It is a decentralized ledger that records all transactions made using digital currencies. Here are some commonly asked questions about blockchain in crypto:
1. How does a blockchain work in cryptocurrency?
A blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information about digital transactions. When a transaction is made, it is confirmed by a network of computers, known as nodes. These nodes validate the transaction by solving complex mathematical algorithms. Once the transaction is validated, it is added as a block to the blockchain. Each block contains a unique identifier, called a hash, and a reference to the previous block. This creates a secure and transparent record of all transactions.
In cryptocurrency, blockchain ensures that each transaction is verified and cannot be altered or deleted. It eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank, to verify and authenticate transactions. Instead, transactions are verified by the decentralized network of nodes, making blockchain a trustless and immutable system.
2. What are the benefits of using blockchain in crypto?
Blockchain technology offers several advantages in the world of cryptocurrency:
Firstly, it enhances security by providing a transparent and immutable record of transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult for hackers to manipulate or tamper with the data.
Secondly, blockchain increases efficiency by eliminating intermediaries. It simplifies the process of verifying and settling transactions, reducing the time and cost involved.
Additionally, blockchain promotes trust among users. As all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be accessed by anyone, it creates a sense of transparency and accountability.
Finally, blockchain enables cross-border transactions without the need for a central authority. This makes it easier and faster to conduct international transactions.
3. Are all cryptocurrencies based on blockchain technology?
No, not all cryptocurrencies are based on blockchain technology. While most popular cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are built on blockchain, there are some exceptions. For example, Ripple uses a distributed consensus ledger called the Ripple Protocol, which is not a traditional blockchain. However, the majority of cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology for their operations.
It’s important to note that blockchain is not limited to cryptocurrencies. The technology has various potential applications beyond digital currencies, including supply chain management, voting systems, and decentralized applications.
4. What is the role of miners in the blockchain?
Miners play a crucial role in the blockchain network. They are responsible for validating and adding transactions to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, known as proof-of-work algorithms. By solving these algorithms, they verify the authenticity of transactions and add them to the blockchain as blocks.
Miners are incentivized for their work through mining rewards. In cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, miners receive newly minted coins as a reward for their computational efforts. This process not only validates transactions but also secures the network against potential attacks.
5. Can blockchain be hacked?
While blockchain technology is highly secure, it is not entirely immune to hacking. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it extremely difficult for hackers to tamper with the data. However, certain vulnerabilities can be exploited.
One potential vulnerability is a 51% attack, where a single entity or group controls more than half of the network’s computing power. This could allow them to manipulate transactions or double-spend coins. However, such attacks are highly unlikely and become increasingly difficult as the network grows in size and decentralization.
It’s worth noting that most successful attacks on blockchain networks have targeted vulnerabilities in other areas, such as user wallets or cryptocurrency exchanges, rather than directly attacking the blockchain itself.
Blockchain And Cryptocurrency Explained In 10 Minutes | Blockchain And Cryptocurrency | Simplilearn
Summary
So, remember, a blockchain is like a special digital notebook that keeps track of transactions. It’s secure because it uses math and computers to make sure everything is accurate. Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, use blockchains to keep a record of who owns what. This helps prevent cheating and fraud. Blockchains are changing the way we think about money and how we do business online. It’s like a super reliable digital ledger that anyone can see, making it a trusted way to keep track of things. In the future, we might see blockchains being used for lots of other important things like voting or keeping medical records safe. Exciting stuff!